Storage Resources¶
StarlingX OpenStack uses storage resources on the controller-labelled master hosts, the compute-labeled worker hosts, and on storage hosts if they are present.
The storage configuration for StarlingX OpenStack is very flexible. The specific configuration depends on the type of system installed, and the requirements of the system.
Storage Services and Backends¶
The figure below shows the storage options and backends for StarlingX OpenStack.
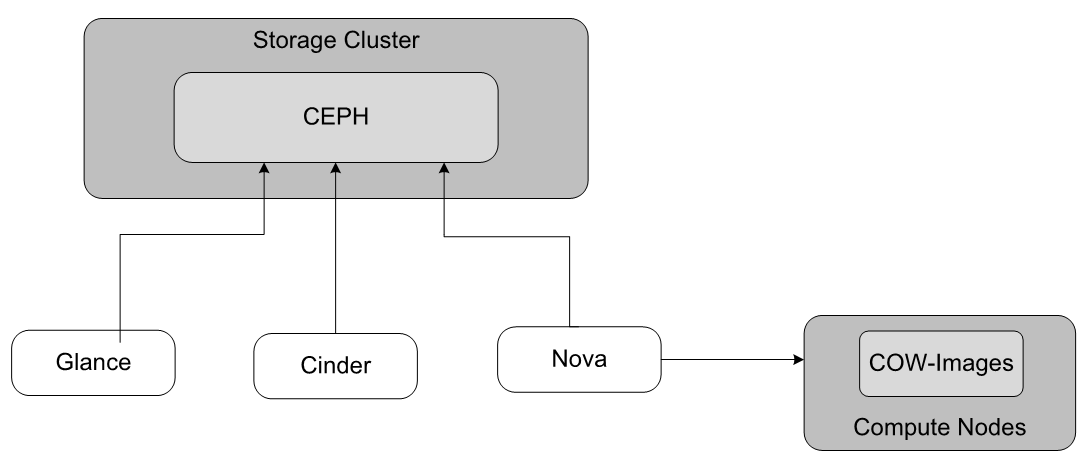
Each service can use different storage backends.
- Ceph
This provides storage managed by the internal Ceph cluster. Depending on the deployment configuration, the internal Ceph cluster is provided through OSDs on StarlingX OpenStack master / controller hosts or storage hosts.
Service |
Description |
Available Backends |
|---|---|---|
Cinder |
|
|
Glance |
|
|
Nova |
|
|
Uses of Disk Storage¶
- |prod-os| System
The StarlingX OpenStack system containers use a combination of local container ephemeral disk, Persistent Volume Claims backed by Ceph and a containerized HA mariadb deployment for configuration and database files.
- VM Ephemeral Boot Disk Volumes
When booting from an image, virtual machines by default use local ephemeral disk storage on computes for Nova ephemeral local boot disk volumes built from images. These virtual disk volumes are created when the VM instances are launched. These virtual volumes are destroyed when the VM instances are terminated.
A host can be configured to instead support ‘remote’ ephemeral disk storage, backed by Ceph. These virtual volumes are still destroyed when the VM instances are terminated, but provide better live migration performance as they are remote.
- VM Persistent Boot Disk Volumes
When booting from Cinder volumes, virtual machines can use the Ceph-backed storage cluster for backing Cinder boot disk volumes. This provides permanent storage for the VM root disks, facilitating faster machine startup, faster live migration support, but requiring more storage resources.
- VM Additional Disk
Virtual machines can optionally use local or remote ephemeral disk storage on computes for additional virtual disks, such as swap disks. These disks are ephemeral; they are created when a VM instance is launched, and destroyed when the VM instance is terminated.
- VM block storage backups
Cinder volumes can be backed up for long term storage in a separate Ceph pool.
Storage Locations¶
The various storage locations for StarlingX OpenStack include:
- Controller Hosts
In the Standard with Controller Storage deployment option, one or more disks can be used on controller hosts to provide a small Ceph-based cluster for providing the storage backend for Cinder volumes, Cinder backups, Glance images, and remote Nova ephemeral volumes.
- Compute Hosts
One or more disks can be used on compute hosts to provide local Nova ephemeral storage for virtual machines.
- Combined Controller-Compute Hosts
One or more disks can be used on combined hosts in Simplex or Duplex systems to provide local Nova Ephemeral Storage for virtual machines and a small Ceph-backed storage cluster for backing Cinder, Glance, and Remote Nova Ephemeral storage.
- Storage Hosts
One or more disks are used on storage hosts to provide a large scale Ceph-backed storage cluster for backing Cinder, Glance, and Remote Nova Ephemeral storage. Storage hosts are used only on StarlingX OpenStack with Dedicated Storage systems.
