Deploy ingress controller¶
Deploying an ingress controller when deploying OpenStack on Kubernetes is essential to ensure proper external access and SSL termination for your OpenStack services.
In the OpenStack-Helm project, we usually deploy multiple ingress-nginx controller instances to optimize traffic routing:
In the kube-system namespace, we deploy an ingress controller that monitors ingress objects across all namespaces, primarily focusing on routing external traffic into the OpenStack environment.
In the openstack namespace, we deploy an ingress controller that handles traffic exclusively within the OpenStack namespace. This instance plays a crucial role in SSL termination for enhanced security between OpenStack services.
In the ceph namespace, we deploy an ingress controller that is dedicated to routing traffic specifically to the Ceph Rados Gateway service, ensuring efficient communication with Ceph storage resources.
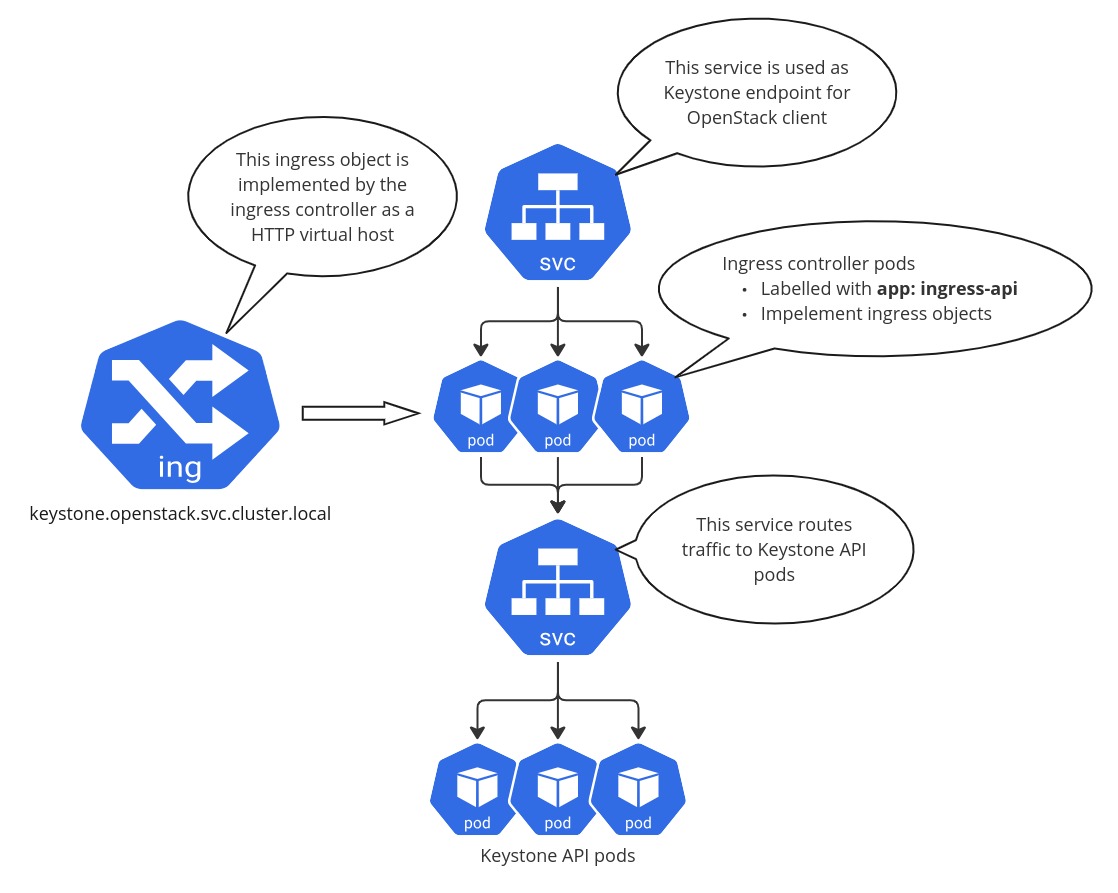
You can utilize any other ingress controller implementation that suits your needs best. See for example the list of available ingress controllers. Ensure that the ingress controller pods are deployed with the app: ingress-api label which is used by the OpenStack-Helm as a selector for the Kubernetes services that are exposed as OpenStack endpoints.
For example, the OpenStack-Helm keystone chart by default deploys a service that routes traffic to the ingress controller pods selected using the app: ingress-api label. Then it also deploys an ingress object that references the IngressClass named nginx. This ingress object corresponds to the HTTP virtual host routing the traffic to the Keystone API service which works as an endpoint for Keystone pods.
To deploy these three ingress controller instances you can use the script ingress.sh
cd ~/osh/openstack-helm
./tools/deployment/common/ingress.sh
