Overcloud Major Upgrade Workflow and CLI¶
The purpose of this documentation is to deep-dive into the code which delivers the major upgrade workflow in TripleO. For information about the steps an operator needs to perform when running this upgrade please see the operator docs.
The major upgrade workflow is delivered almost exclusively via Ansible playbook invocations on the overcloud nodes. Heat is used to generate the Ansible playbooks (during the ‘prepare’ command at the beginning, and ‘converge’ command at the end of the upgrade). The Queens_upgrade_spec may be of interest in describing the design of the workflow.
CLI code is in python-tripleoclient, mistral workflows and actions in tripleo-common, and upgrade tasks in tripleo-heat-templates. The following sections dive into the details top-down per individual CLI commands which are used to deliver the major upgrade:
You might also find it helpful to consult this high-level diagram as you read the following sections:
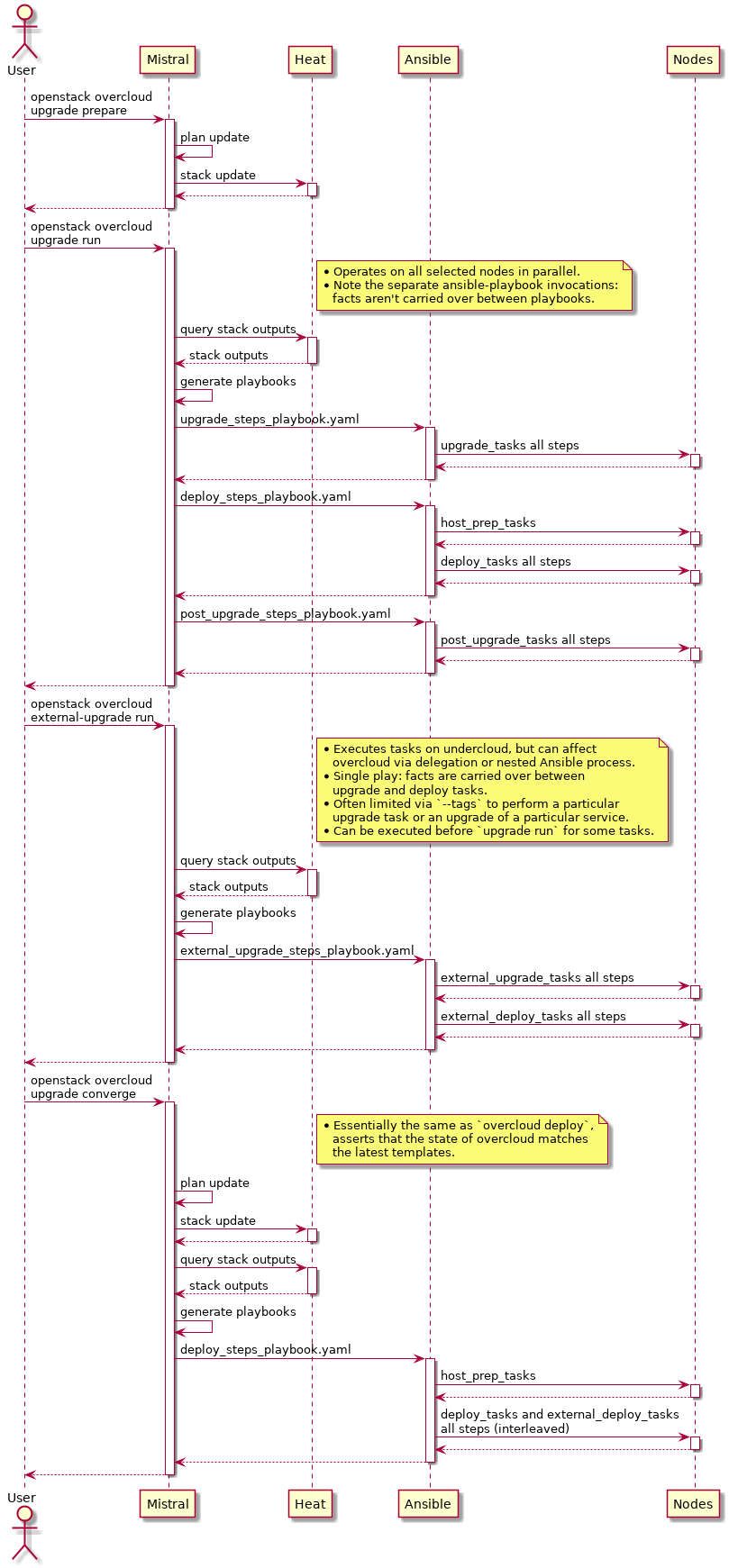
openstack overcloud upgrade prepare $ARGS¶
The entry point for the the upgrade CLI commands, prepare, run and converge, is given in the python-tripleoclient setup.cfg. All three are also defined in the same file, overcloud-upgrade.py.
The ‘prepare’ Heat stack update does not apply any TripleO configuration and is exclusively used to generate the Ansible playbooks that are subsequently invoked to deliver the upgrade.
As you can see the UpgradePrepare class inherits from DeployOvercloud. The reason for this is to prevent duplication of the logic concerned with validating the configuration passed into the prepare command (all the -e env.yaml files), as well as updating_the_swift_stored_plan with the overcloud configuration.
The prepare_env_file is automatically prepended to the list of environment files passed to Heat (as specified by prepare_command_prepends). It contains resource_registry and parameter_defaults which are intended to be in effect during the upgrade.
As a result the UpgradePrepare class inherits all the Deploy_parser_arguments,
including --stack and -e for the additional environment files. We explicitly
set the update_plan_only argument so that the Heat stack update does not get
executed by the parent class and returns after completing all the template
processing.
Instead, the Heat stack update is performed by a mistral workflow. On the client side the hook is in the update method defined in package_update.py. This invokes the package_update_plan mistral workflow in tripleo-common. The package_update_plan workflow has a number of tasks, one of which invokes the heat stack update using the update_stack_action.
Back on the tripleoclient side, we use base_wait_for_messages to listen for messages on the Zaqar_queue that is used by the mistral workflow.
The operator must include all environment files previously used with the overcloud deploy command. It is especially important that the operator includes the environment file containing the references for the target version container images.
See the operator docs for pointers to how that file is generated and for reference it will look something like
parameter_defaults: DockerAodhApiImage: 192.168.24.1:8787/queens/centos-binary-aodh-api:current-tripleo-rdo DockerAodhConfigImage: 192.168.24.1:8787/queens/centos-binary-aodh-api:current-tripleo-rdo DockerAodhEvaluatorImage: 192.168.24.1:8787/queens/centos-binary-aodh-evaluator:current-tripleo-rdo DockerAodhListenerImage: 192.168.24.1:8787/queens/centos-binary-aodh-listener:current-tripleo-rdo
Once the Heat stack update has been completed successfully and the stack is in UPDATE_COMPLETE state, you can download the configuration ansible playbooks using the config download cli
[stack@521-m--undercloud ~]$ source stackrc (undercloud) [stack@521-m--undercloud ~]$ openstack overcloud config download --config-dir MYCONFIGDIR The TripleO configuration has been successfully generated into: MYCONFIGDIR/tripleo-gep7gh-config
and you can inspect the ansible playbooks which are used by the upgrade run before executing them.
openstack overcloud upgrade run $ARGS¶
Unlike the first step in the workflow, the upgrade prepare, the UpgradeRun class does not inherit from DeployOvercloud. There is no need for the operator to pass all the environment files and configuration here. The template processing and update of the stack and swift stored plan have already taken place. The ansible playbooks are ready to be retrieved by config download as demonstrated above. The upgrade run operation thus will simply execute those ansible playbooks generated by the upgrade prepare command, against the nodes specified in the parameters.
Either --nodes or --roles parameters are used to limit the ansible
playbook execution to specific nodes. Both --roles and --nodes are
used by ansible with the tripleo-ansible-inventory. This creates the
ansible inventory based on the Heat stack outputs, so that for example
Controller and overcloud-controller-0 are both valid values for
the ansible-playbook --limit parameter.
See overcloud upgrade run for additional information.
As documented in the major upgrade documentation and the nodes_or_roles_helptext,
the operator must use --roles for the controllers. Upgrading the
controlplane, one node at a time is currently not supported, mainly
due to limitations in the pacemaker cluster upgrade which needs to
occur across all nodes in the same operation. The operator may use
--roles for non controlplane nodes or may prefer to specify one or
more specific nodes by name with --nodes. In either case the value
specified by the operator is simply passed through to ansible as the
limit_hosts parameter.
The --ssh-user and all other parameters are similarly
collected and passed to the ansible invocation which starts on the client side
in the run_update_ansible_action method call. The --skip-tags
parameter can be used to skip certain ansible tasks with the ansible-skip-tags
ansible-playbook parameter. The allowed --skip-tags values are restricted
to a predefined set, validated against
MAJOR_UPGRADE_SKIP_TAGS. Finally, the --playbook parameter as the name
suggests is used to specify the ansible playbook(s) to run. By default and
as you can see in the definition, this defaults to a special value ‘all’
which causes all-upgrade-playbooks-to-run. The value of all_playbooks
in that previous reference, is stored in the MAJOR_UPGRADE_PLAYBOOKS constant.
As with the upgrade prepare, for upgrade run a mistral workflow is used to perform the ‘main’ operation, which in this case is execution of the ansible playbooks. On the client side the update_nodes_workflow_invocation is where mistral is invoked and takes as workflow input the various collected parameters described above. You can see that the update_nodes_workflow which lives in tripleo-common has parameters defined under the ‘input:’ section which correspond to the openstack overcloud upgrade run parameters.
There are two main tasks in the update_nodes_workflow, the download-config_action which is invoked in a first ‘download_config’ task, and the ansible-playbook_action action which is invoked in the ‘node_update’ task. This is ultimately where ansible-playbook-is-executed with processutils.execute.
Finally back on the client side we listen for messages on the run_zaqar_queue before declaring the upgrade-run-success!
openstack overcloud external-upgrade run $ARGS¶
The external-upgrade run command is used to upgrade the services whose deployment (and upgrade) procedure is not tied to execution on particular overcloud nodes. The deployment/upgrade procedures are thus executed from the undercloud, even though a full overcloud inventory is available for use.
The external upgrade playbook first executes external_upgrade_tasks and then external_deploy_tasks. The execution happens within the same Ansible play, so facts from external_upgrade_tasks are carried over to external_deploy_tasks. This is a mechanism which will allow you to amend what your deploy tasks do based on whether an upgrade is being run or not.
Often it’s not desirable to run the tasks for all services at the same
time, so external-upgrade run supports --tags argument to limit
which tasks are run.
The mechanisms of external-upgrade and external-update commands and Ansible tasks are the same, but two commands and task hooks are provided because generally in OpenStack we distinguish minor update vs. major upgrade workflows. If your service only has one type of upgrade, you can make the external_update_tasks the same as external_upgrade_tasks by using YAML anchors and references.
openstack overcloud upgrade converge $ARGS¶
The UpgradeConverge class like the UpgradePrepare class also inherits from the DeployOvercloud class thus getting all of its parameters and template processing. The operator needs to pass in all Heat environment files used as part of the upgrade prepare including the container images file.
The main objective of the upgrade converge operation is to unset the upgrade specific parameters that have been set on the overcloud Heat stack as part of prepare. These are unset using the converge_env_file which is included in the list of client_converge_env_files passed to the Heat stack update.
The ‘converge’ applies all TripleO configuration against all overcloud nodes and thus serves as a sanity check that the overcloud was successfully upgraded, since the same configuration will already have been applied. The ‘converge’ will also leave the Heat stack in a good state for subsequent updates, for instance scaling to add nodes.
As these values are set in parameter_defaults a Heat stack update is required against the overcloud Heat stack to explicitly unset them. In particular and as pointed out in the operator_converge_docs until converge has completed, any operations that require a Heat stack update will likely fail, as the ‘noop’ of the DeploymentSteps in the prepare_env_file in particular means none of the usual docker/puppet/* config is applied. Setting something with parameter_defaults means it is used until explicitly unset via parameter_defaults as that value will override any other default value specified via the tripleo-heat-templates.
Unlike the prepare command there is no mistral workflow here and instead we rely on the parent DeployOvercloud class to invoke the converge_heat_stack_update and so the implementation is also simpler.
Upgrade CLI developer workflow¶
This section will give some examples of a potential developer workflow for testing fixes or in-progress gerrit reviews against python-tripleoclient, tripleo-common or tripleo-heat-templates for the upgrade workflow. This may be useful if you are working on an upgrades related bug for example.
Making changes to the ansible playbooks¶
If there is a failure running one of the upgrades related ansible playbooks, you might need to examine and if necessary fix the related ansible task. The tasks themselves live in each of the tripleo-heat-templates service manifests, under the upgrade_tasks section of the template outputs. For example see the containerized rabbitmq_upgrade_tasks.
If you make a change in service upgrade_tasks, then to test it you will need to
Patch the tripleo-heat-templates in your environment with the fix
Rerun openstack overcloud upgrade prepare $ARGS, so that the resulting ansible playbooks include your fix.
Finally run the playbooks with openstack overcloud upgrade run $ARGS.
Assuming you are using the default /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates directory for the deployment templates you can use the following as just one example:
# backup tht in case you want to revert - or just yum re-install ;) sudo cp -r /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates \ /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates.ORIG # Apply patch from gerrit e.g. https://review.opendev.org/#/c/563073/ curl -4sSL 'https://review.opendev.org/changes/563073/revisions/current/patch?download' | \ base64 -d | \ sudo patch -d /usr/share/openstack-tripleo-heat-templates/ -p1
Making changes to the upgrades workflow¶
If instead you need to add or fix something in the upgrades workflow itself, for example to handle a new parameter needed passed through to ansible, or any other change, you will need to patch python-tripleoclient and tripleo-common, depending on whether your fixes extend to the mistral workflow too.
There are many ways to patch your environment and the following is a different approach to the one used in the tripleo-heat-templates above where we patched the installed templates in place. In the following examples instead we clone tripleo-common and tripleoclient, patch them using gerrit reviews and then re-install from source.
Note
The following example commands include complete removal and replacement of the installed tripleoclient and tripleo-common!
Patching python-tripleoclient:
# python-tripleoclient - clone source, patch from gerrit and install git clone https://github.com/openstack/python-tripleoclient.git -b stable/queens ~/python-tripleoclient pushd ~/python-tripleoclient # Apply patches from gerrit e.g. https://review.opendev.org/#/c/564267 curl "https://review.opendev.org/changes/564267/revisions/current/patch" | \ base64 --decode > /home/stack/"564267.patch" patch -N -p1 -b -z .first < /home/stack/564267.patch # Remove current version and re-install sudo rm -rf /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/python_tripleoclient* sudo rm -rf /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tripleoclient sudo python setup.py clean --all install popd
Patching tripleo-common:
Note
After switching to containerized undercloud, local tripleo-common changes to be applied in all Mistral containers.
# tripleo-common - clone from source, patch from gerrit and install git clone https://github.com/openstack/tripleo-common -b stable/queens pushd ~/tripleo-common # Apply patches from gerrit e.g. https://review.opendev.org/#/c/562995 curl "https://review.opendev.org/changes/562995/revisions/current/patch" | \ base64 --decode > /home/stack/"562995.patch" patch -N -p1 -b -z .first < /home/stack/562995.patch # Remove current version and re install sudo rm -rf /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tripleo_common* sudo python setup.py clean --all install popd sudo cp /usr/share/tripleo-common/sudoers /etc/sudoers.d/tripleo-common
Finally you need to update the mistral workbooks with the newly installed versions. In code block above, the tripleo-common change at 562995 has changed package_update.yaml and so that is what we need to update here:
mistral workbook-update /usr/share/tripleo-common/workbooks/package_update.yaml # Since entry_points.txt is affected next steps are required: # Re populate mistral db and restart services sudo mistral-db-manage populate sudo systemctl restart openstack-mistral-api.service sudo systemctl restart openstack-mistral-engine.service sudo systemctl restart openstack-mistral-executor.service
